What is the difference between industrial cable and data cable?
In the modern world of connectivity and infrastructure, cables are the unsung heroes that keep our industries, businesses, and daily lives running smoothly. However, not all cables are created equal. Two types that often cause confusion are industrial cables and data cables. While they may look similar at first glance, their designs, functions, and applications are vastly different. This article will delve into the key differences between them, providing practical insights for anyone seeking to understand their unique roles.
1. Definition and Primary Purpose
Industrial cables are specifically engineered to withstand harsh environments in industrial settings. Their primary purpose is to transmit power, control signals, or data in environments where factors like extreme temperatures, moisture, chemicals, mechanical stress, and electromagnetic interference (EMI) are prevalent. These cables are the backbone of industrial machinery, allowing for the operation and coordination of heavy equipment, manufacturing lines, and industrial automation systems.
Data cables, on the other hand, are designed primarily for the transmission of digital data. Their main function is to carry information between electronic devices such as computers, routers, switches, servers, and various consumer electronics. The focus here is on high-speed, reliable, and accurate data transfer, with less emphasis on withstanding extreme environmental conditions compared to industrial cables.
**
An industrial cable being used in a factory environment, surrounded by machinery and harsh conditions.
2. Design and Construction
The design and construction of industrial cables are centered around durability and resilience. They typically feature thick, robust insulation and sheathing materials. Common materials used include PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), polyurethane, and rubber, which offer resistance to chemicals, oils, abrasion, and high temperatures. Some industrial cables also have additional layers of protection, such as metal braids or armor, to shield against mechanical damage and EMI.
Data cables, in contrast, have a more streamlined design. Their construction focuses on minimizing signal loss and interference to ensure efficient data transmission. They often consist of multiple twisted pairs of copper wires (in the case of Ethernet cables) or optical fibers (for fiber optic cables). The insulation is usually made of materials like polyethylene or Teflon, which have good dielectric properties to reduce signal attenuation. The sheathing is generally thinner and more flexible, suitable for indoor use in relatively controlled environments.
**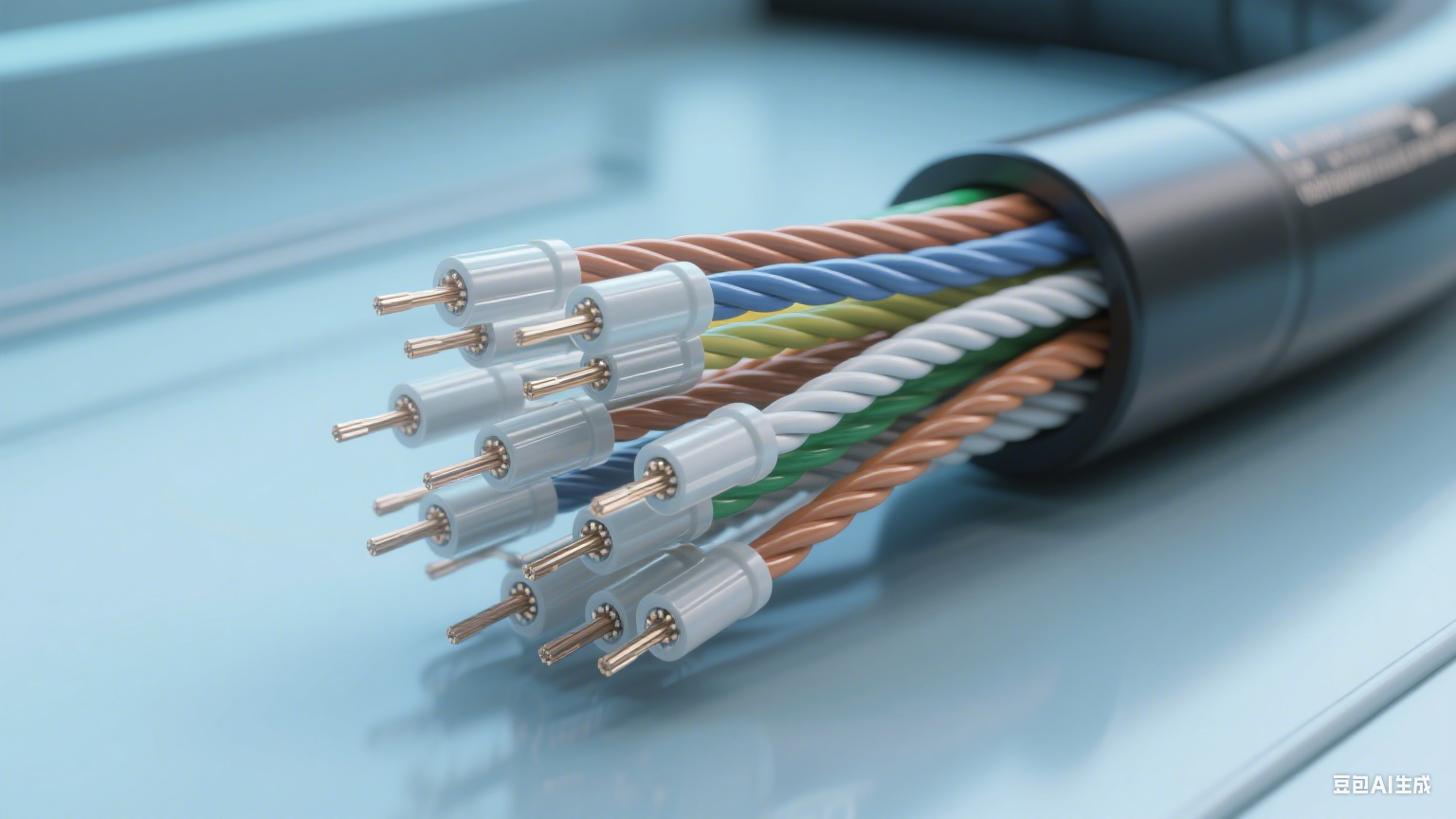
A data cable connecting a computer to a router, showcasing its flexible and compact design.
3. Performance Characteristics
When it comes to performance, industrial cables prioritize reliability under extreme conditions. They are designed to maintain their functionality over a wide range of temperatures, often from -40°C to 105°C or higher. They also have high tensile strength and can withstand significant mechanical stress, such as being pulled, bent, or crushed. Additionally, industrial cables are engineered to resist EMI, which is crucial in industrial environments where numerous electrical devices and machinery can generate interference.
Data cables, performance is measured by their data transfer rate, bandwidth, and signal integrity. For example, Ethernet cables like Cat 6 can support data transfer speeds of up to 10 Gbps at a maximum distance of 55 meters, while fiber optic cables can transmit data at much higher speeds over longer distances, often tens or hundreds of kilometers. Signal loss and latency are key concerns for data cables, and their design ensures that these factors are minimized to provide fast and accurate data transmission.
4. Application Scenarios
Industrial cables find their applications in a wide range of industrial sectors. They are used in manufacturing plants to connect robots, conveyor belts, and control systems. In the energy industry, they are employed in power generation facilities, oil and gas refineries, and renewable energy installations to transmit power and control signals. They are also used in transportation systems such as railways, where they need to withstand vibration and harsh weather conditions.
Data cables are ubiquitous in office environments, data centers, and homes. They connect computers to printers, modems to routers, and servers in data centers to ensure seamless communication and data sharing. They are also used in telecommunications networks to transmit voice, video, and data over long distances.
5. Compliance and Standards
Industrial cables must comply with strict industry standards to ensure their safety and performance in harsh environments. These standards vary depending on the industry and application but often include requirements for flame resistance, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength. Examples of such standards include those set by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA).
Data cables are also subject to standards that govern their performance and compatibility. For Ethernet cables, standards like TIA/EIA-568 define the specifications for different categories of cables, ensuring that they can support specific data transfer speeds and distances. Fiber optic cables adhere to standards set by organizations such as the Telecommunication Industry Association (TIA) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
Conclusion
In summary, industrial cables and data cables are distinct in their design, purpose, performance, and applications. Industrial cables are built to withstand harsh industrial environments and focus on reliable transmission of power and control signals, while data cables are designed for high-speed, accurate data transfer in more controlled settings.
Understanding these differences is essential when selecting the right cable for a particular application. For businesses and industries in need of high-quality cables that meet these specific requirements, FRS brand factory is the ideal choice. FRS specializes in producing both industrial cables and data cables, adhering to strict standards to ensure durability, performance, and reliability. Whether you need cables for a tough industrial environment or for efficient data transmission, FRS has you covered with top-notch products tailored to your needs.













